Colorfastness
Also known as dyeing fastness. It refers to the resistance of textile color to various effects in the process and use. According to the discoloration of the sample and undyed lining fabric staining to assess the fastness level.

How to test colorfastness?
1. Washing color fastness

The specimens are sewn together with standard lining fabrics, washed, cleaned and dried under suitable conditions of temperature, alkalinity, bleaching and rubbing to enable test results to be obtained in a short period of time.
Different test methods have different temperatures, alkalinity, bleaching and rubbing conditions and specimen size, the specific ones should be selected according to the test standard and customer requirements. The colors with poor washing colorfastness in general are emerald blue, bright blue, navy blue, etc.
2. Dry cleaning color fastness

The same color fastness as the wash, but the water wash is changed to dry clean.
3. Rubbing color fastness

The specimen will be placed on the rubbing fastness instrument, in a certain pressure with the standard rubbing white cloth a certain number of times, each group of specimens is required to do dry rubbing colorfastness and wet rubbing colorfastness. The color is stained on the standard friction white cloth with a gray card rating, the resulting grade is the measured friction colorfastness.
4. Sunlight fastness
Textiles are usually exposed to light when in use, and light destroys dyes and causes “fading”, making colored textiles discolored, generally lighter and darker. The fastness to sunlight test is to put the specimen with different fastness levels of blue wool standard cloth together under the specified conditions of sunlight exposure, the specimen will be compared with the blue wool cloth to assess the light fastness, the higher the level of blue wool standard cloth, the more light-resistant.
5. Colorfastness to sweat stains

The specimens are sewn together with the standard lining fabric, placed in the sweat solution and then clamped on the sweat fastness meter, placed in the oven at a constant temperature, then dried and rated with a gray card to obtain the test results.
6. Water stain colorfastness
To treat specimens in water instead of sweat as above.
7. Non-chlorine bleaching colorfastness
After washing the fabric under non-chlorine bleaching conditions, assess the degree of color change.
8. Stamping colorfastness
After covering the dry specimen with cotton lining fabric, it is pressed for a certain time in the heating device at the specified temperature and pressure, and then the color change of the specimen and the color staining of the lining fabric are evaluated by the gray sample card. Hot pressing colorfastness has dry pressure, tide pressure, wet pressure, according to different customer requirements and test standards to choose the test method.
Types of Color Fastness Tests and Fastness Analysis

The color fastness of fabrics is related to the type of fiber, yarn structure, fabric organization, printing and dyeing methods, dye types and the size of external forces.
The color fastness test generally includes light fastness, weather fastness, washing fastness, rubbing fastness, sweat fastness, etc. Sometimes there are some special requirements of colorfastness according to different textiles or different use environments.
Usually, when the colorfastness test is carried out, except for the light fastness, which is grade 8, the rest are grade 5. The higher the grade, the better the colorfastness.
1. Light fastness
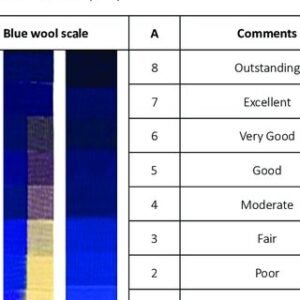
Lightfastness refers to the degree to which colored fabrics are discolored by sunlight. The test method is to compare the fading degree of the sample after simulating sunlight exposure with the standard color sample, and it is divided into 8 grades, 8 grades are the best results, and 1 grade is the worst. Fabrics with poor lightfastness should not be exposed to the sun for a long time and should be dried in a ventilated place.
2. Washing fastness
Washing fastness refers to the degree of the color change of the dyed fabric after washing. Usually, the gray grading sample card is used as the evaluation standard, that is, it relies on the color difference between the original sample and the sample after fading to judge. Washing fastness is divided into 5 grades, with 5 grades being the best and 1 grade being the worst. The washing fastness of poor fabrics should be dry-cleaned. If wet cleaning is used, more attention should be paid to the washing conditions, such as the washing temperature should not be too high, and the washing time should not be too long.
3. Rub fastness
Rubbing fastness refers to the degree of color loss of dyed fabric after rubbing, which can be all dry rubbing and wet rubbing. Rubbing fastness takes the white cloth staining degree as the evaluation principle, and is divided into 5 levels, the larger the value, the better the rubbing fastness.
4. Perspiration fastness

Perspiration fastness refers to the degree of fading of dyed fabrics after a small amount of perspiration.
5. Ironing fastness
It refers to the degree of discoloration or fading of dyed fabrics when ironing.
6. Sublimation fastness
It refers to the degree of sublimation that occurs in the storage of dyed fabrics.

